Explore nutrient-rich superfoods that strengthen your immune system and keep you healthy year-round.
In India, we are fortunate to experience the beauty of four distinct seasons—winter, summer, monsoon, and post-monsoon. However, with each seasonal shift, our health often faces challenges, and our immune system may become compromised. While modern medicines are available, frequent use can sometimes bring unwanted side effects. That’s why one of the best ways to care for our health is by turning to traditional wisdom.
Since childhood, I have seen how our parents and grandparents prepared us for seasonal changes with simple yet powerful home remedies. These remedies often came in the form of fruits, vegetables, and other natural ingredients that boosted our immunity and helped us welcome the new season with strength and positivity.
As a researcher, I strongly believe in the benefits of natural sources of immunity. Today, I would like to share some of these traditional practices that I have learned from my family, which continue to inspire me to live in harmony with nature.
Today, I will share my top 12 immune-boosting foods that help strengthen my immunity and protect me during the changing seasons.
1. Ginger
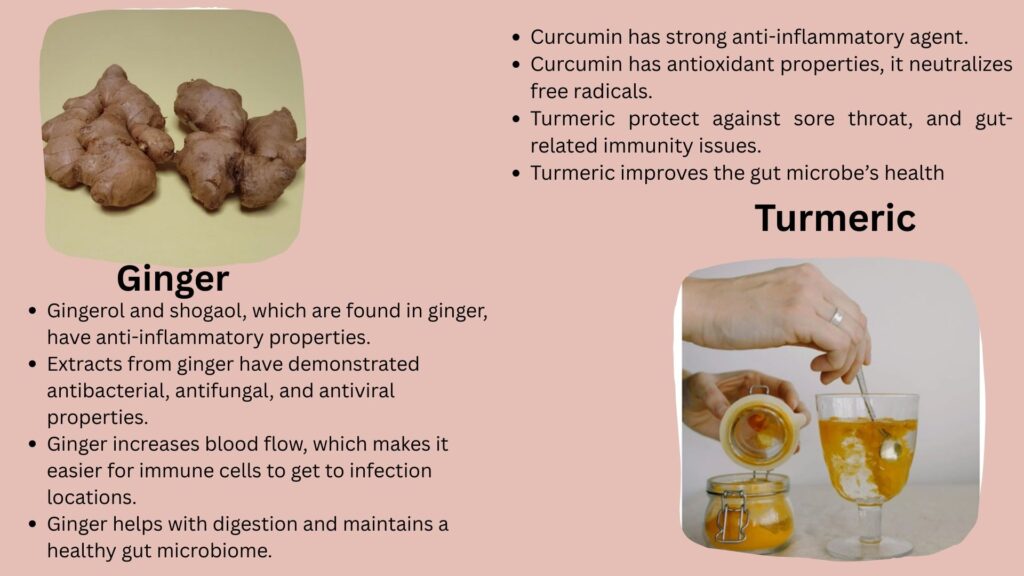
Zingiber officinale, commonly known as ginger, is a flowering plant whose rhizome is primarily used as a spice and possesses various medicinal benefits, including the management of diabetes, cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, cerebrovascular events, and depression.
The main pungent components found in ginger rhizomes are called gingerols, and they are well known for their nutritional and health benefits.
Gingerol undergoes dehydration reaction to form shogaols. Which give the strong pungent flavor ot dried ginger.
Both gingerols and shogaols have a variety of biological properties, including anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, anti-oxidant, anti-cancer, and anti-microbial properties as well as actions related to the central nervous system.
How Ginger Boost Immunity
Anti-inflammatory effects
Gingerol and shogaol, which are found in ginger, have anti-inflammatory properties. By doing this, immune system is not overloaded and work more effectively.
Antioxidant activity
Ginger protects against oxidative stress, by eliminating free radicals. which weakens immunity.
Protect from bacteriaa, fungal and viral infection
Extracts from ginger helps against infections such as the common cold, sore throat, and moderate flu.
Ginger increases blood flow, which makes it easier for immune cells to get to infection locations.
Supports gut health
Ginger helps with digestion and maintains a healthy gut microbiome.
Different ways to consume Ginger
Ginger tea – Fresh ginger slices boiled in water with honey and lemon.
Golden milk– Boil milk with ginger, half spoon turmeric and a pinch of black pepper (pepper boosts absorption of curcumin) and drink before going to bed.
Ginger is a common ingredient in Indian cuisine and is widely used in curries, soups, stir-fried sabji, tea, and many other dishes.”
Ginger shots – Blend ginger with lemon and a bit of honey for a concentrated boost.
Precaution
Too much ginger may cause acidity or stomach irritation.
Avoid excessive intake if you’re on blood thinners or have gallstones — check with your doctor in that case.
2. Turmeric or Haldi
Turmeric or Haldi (Curcuma longa) produces a secondary metabolite called curcumin, which helps boost immunity by acting as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent.
Haldi reduces oxidative stress, inhibits inflammatory pathways, and modulates immune cells such as macrophages and T-cells.
Turmeric also produces other secondary metabolite such terpenoids and flavonoids, which protect against infections and inflammatory conditions.
Turmeric, also known as haldi, is one of the most potent natural immune enhancers. It was utilized in Ayurveda and is now supported by modern studies.
Related article: Turmeric: Indian Saffron
How Turmeric Boosts Immunity?
Curcumin has antioxidant properties, it neutralizes free radicals, protecting immune cells from damage.
Curcumin shows antimicrobial effects, it fights against bacteria, fungi, and even some viruses in lab studies.
Haldi or turmeric protect against respiratory infections, sore throat, and gut-related immunity issues.
Turmeric improves the gut microbe’s health. This improves overall protection because the gut contains about 70% of immunity.
Different ways to consume Turmeric
Golden milk– Boil milk with ginger, half spoon turmeric and a pinch of black pepper (pepper boosts absorption of curcumin) and drink before going to bed.
Turmeric tea – Boil fresh turmeric root (or powder) with ginger, add lemon & honey.
Cooking – Add Haldi to curries, soups, rice, or vegetables daily.
Supplements – Curcumin capsules (with piperine) are available, but dosage should be doctor-guided.
Precautions
Excess use may cause acidity or stomach upset.
People on blood thinners (like warfarin/aspirin) or with gallbladder issues should consult a doctor first.
Turmeric works best as a daily small dose (in food/tea), not as a one-time high dose.
Related article: 14 Benefits of Turmeric (Indian Saffron
3. Garlic
Garlic or Lahsun (Allium sativum) contain allicin which boosts immunity. Allicin activated when garlic is crushed or chewed.
The sulfur-containing molecule alliin in garlic is broken down into allicin when it is chewed or crushed.
Allicin is a vital bioactive ingredient that helps garlic’s immune-boosting qualities.
Allicin improve white blood cell counts, and possess anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that help protect the body.
Allicin improve the immune system, helping to fight off viruses that cause colds and the flu.
Garlic consumption may lower the chance of becoming sick, shorten the duration of illness, and lessen the severity of flu and cold symptoms.
How Garlic Boost immune system
To help them fight off infections, garlic activates a variety of immune cells, including as lymphocytes, natural killer (NK) cells, and macrophages.
Garlic can block inflammatory factors and protect against oxidative damage, reducing inflammation and supporting overall immune function.
Garlic can improve the count of total white blood cells (WBC), which are crucial for your body’s defense against pathogens.
Besides allicin, garlic is a rich source of vitamins and minerals, including Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B6, folate, magnesium, phosphorus, sodium, zinc, iron, and manganese.
How to consume Garlic
To get a raw and powerful dosage of garlic’s immune-boosting properties, add chopped or crushed garlic to spreads, dips, or salad dressings.
In many dishes, roasted garlic with olive oil is used, making them both delicious and healthy.
Garlic pickle is made by mixing peeled garlic cloves with roasted spices, along with lemon juice and mustard oil. The mixture is stored in a clean jar and kept in sunlight for a few days. This tangy-spicy pickle not only enhances taste but also boosts immunity and digestion.
Garlic tea by crushed garlic in hot water, often enhanced with honey, lemon, or other spices.
Garlic used in soups, curry, stews, sauces, and other dishes to add flavor while also gaining its health benefits.
Precaution
Excess garlic may cause acidity, heartburn, stomach upset, or bad breath. Overuse can thin the blood, so people on blood-thinning medications should be cautious. Always consume in moderation to enjoy its health benefits safely.
4. Citrus fruit
Citrus fruit like, orange, lemon, tangerine, sweet lime (Mosambi), grapefruit, Amla, kinnow contain secondary metabolites like Vitamin C, flavonoids, limonoids, and phenolic acids that enhance immunity through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial actions, supporting various immune cell functions and protecting against cellular damage.
Citrus fruits help to improve immune system, regulate inflammation, improve white blood cell.
How citrus fruits Boost immune system
Citrus fruits are a major source of vitamin C or Ascorbic acid, which is an important antioxidant and essential for immune cell activity. It helps in producing antibodies.
Citrus fruits contain Flavonoids such as hesperidin and naringenin, that have significant anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Citrus fruits contain limonoids, which promote health by acting as antioxidants, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer agents, thereby supporting and strengthening the immune system.
Phenolic Acids present in citrus fruits exhibit anti-inflammatory and protective effects.
How citrus fruits boost Immune System
Citrus fruits acts as an Antioxidant Activity eliminate free radicals that can damage cells and contribute to inflammation.
Citrus contains secondary metabolites with antibacterial qualities that may help the immune system in fending off bacterial and fungal diseases.
Citrus fruits support for immune cells by improving white blood cells (leukocytes), phagocytes, natural killer cells, and T-lymphocytes, all of which are crucial for a robust immune response.
Vitamin C supports skin health; since skin is the body’s first barrier against germs, healthy skin.
How to consume citrus fruits
Fresh orange or sweet lime juice in the morning.
Warm lemon water with honey (good for throat and immunity).
Amla juice or chutney daily in small amounts.
Add lemon to salads, soups, or herbal teas.
Eat whole fruits (better than packaged juices with added sugar).
Precautions
Too much citrus may cause acidity or enamel erosion in teeth (rinse mouth after juices).
People with citrus allergies should avoid.

5. Spinach
Spinach or Palak (Spinacia oleracea) is a superfood when it comes to immunity boosting.
How Spinach Strengthens Immunity
Palak is rich in vitamin C, just like citrus fruits, which helps in the production of white blood cells (WBCs).
Palak contain vitamin A (from beta-carotene) that maintains the health of skin and mucous membranes (your first line of defense against infections). It supports proper functioning of immune cells.
Palak contain vitamin E which is powerful antioxidant that protects immune cells from damage.
Palak contain Folate (Vitamin B9) which is crucial for the formation of new cells, including immune cells.
Palak contain iIron & Magnesium. Iron helps transport oxygen in blood, keeping cells energized to fight infections. Magnesium regulates immune response and reduces inflammation.
Palak contain flavonoids and carotenoids lutein, zeaxanthin, and beta-carotene. It Fight free radicals and prevent oxidative stress, which weakens immunity.
Palak contain saponins that possess immunostimulatory effects by enhancing macrophage and lymphocyte activity.
Quercetin, abundant in spinach has been studied for enhancing resistance to viral infections.
Precursors of Vitamin A, which is essential for mucosal immunity and healthy epithelial barriers (skin, gut, respiratory lining).
Lutein and zeaxanthin act as antioxidants, protecting immune cells from damage.
How to consume palak or spinach
Cook spinach at medium flame or steaming or sautéing retains nutrients (avoid overcooking).
Spinach use in smoothies/juices in which blend fresh spinach with apple, orange, or ginger. It is flavourful with immune booster
Spinach can be used in soups and dals in which add to lentils, broths, or vegetable soups.
Spinach can consume as salads in which young spinach leaves can be eaten raw.
Precautions
Spinach is high in oxalates, which may contribute to kidney stones in sensitive people so don’t overconsume raw spinach daily.
Pairing spinach with vitamin C-rich foods (lemon, orange, tomato) increases iron absorption.
6. Broccoli
Broccoli, also known as Brassica oleracea (Italica Group), is a cool-weather vegetable that is produced for its green flower buds at the ends of thick, edible stems.
How Broccoli Boost Immunity
Broccoli is Vitamin C powerhouse; a single cup of broccoli provides more vitamin C than an orange. Vitamin C also enhances the production of white blood cells (WBCs) and antibodies.
Broccoli produces vitamin A (from beta-carotene) that supports the health of skin and mucosal linings (first barrier against infections).
Broccoli produces vitamin E, a strong antioxidant that protects immune cells from oxidative damage.
Broccoli contains carotenoids such as β-carotene and lutein which as act as antioxidants, It protects cells from oxidative damage and supporting overall cellular health.
Broccoli produces secondary metabolite sulforaphane, one of the most powerful antioxidants found in cruciferous vegetables. It improve the immune system. It has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anticancer effects.
Broccoli produces flavonoids such as quercetin, kaempferol that reduce inflammation, boost antiviral defense, and support gut immunity.
Broccoli also rich source of zinc and selenium. It is essential trace minerals in broccoli that help immune enzymes function properly.
Broccoli have gut-friendly fiber that promotes a healthy gut microbiome. Since ~70% of immunity resides in the gut, this is a major benefit.
Best Ways to consume Broccoli
Lightly steamed (3–5 min) broccoli retains most vitamin C and sulforaphane.
Broccoli consumes as soup with garlic and ginger for combined immunity boost.
Broccoli can be eaten as salads or Stir-fry. Quick cooking keeps nutrients intact.
Broccoli consume as smoothies in which raw broccoli florets can be blended with apple, spinach, and lemon.
Precaution
Protect broccoli overcooking because it destroys vitamin C and sulforaphane, so steaming is best.

7. Blueberries
In North America, a variety of blueberry species, such as Vaccinium myrtilloides, V. angustifolium, and V. corymbosum, grow wild on the forest floor or next to swamps.
How Blueberries Boost Immunity
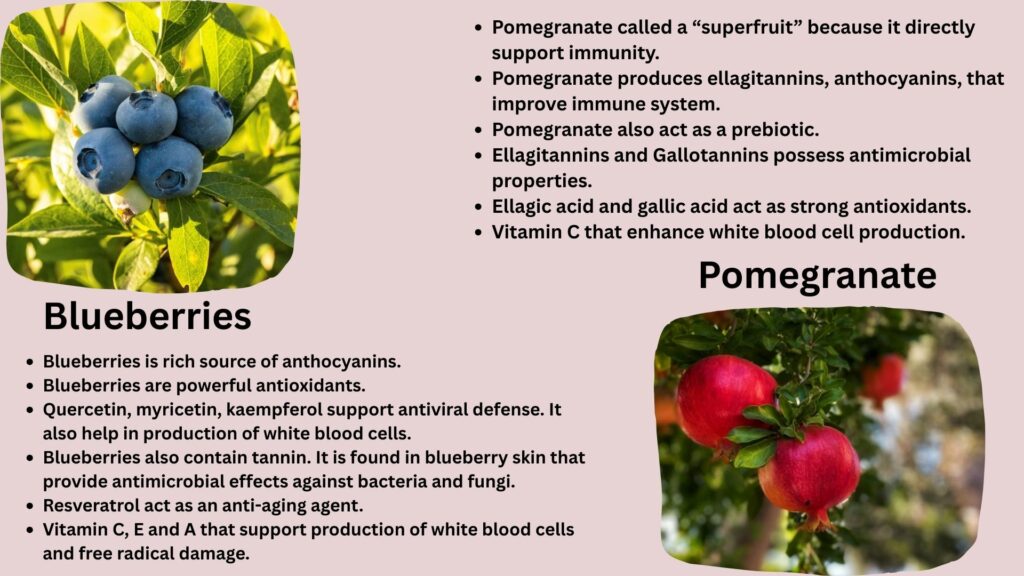
In blue berries blue/ purple color comes from secondary metabolite, anthocyanins. Blueberries is rich source of anthocyanins such as cyanidin, delphinidin, malvidin, peonidin, petunidin
which are powerful antioxidants that protect immune cells from oxidative stress.
blueberries are powerful antioxidants that protect immune cells from oxidative stress. It also have antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects.
Other Flavonoids (non-anthocyanins) such quercetin, myricetin, kaempferol support antiviral defense, reduce inflammation, modulate immune cell signaling. It also help in production of white blood cells.
Blueberries contain phenolic Acids such as chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid. It ac an Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent that regulate immune response.
Blueberries also contain tannins (proanthocyanidins). It is found in blueberry skin that provide antimicrobial effects against bacteria and fungi.
Blueberries contain small amount of resveratrol. It is modulate immune- system and act as an anti-aging agent.
Vitamin C in blueberries supports production of white blood cells (WBCs) and antibodies. It strengthens the skin barrier (first line of defense against pathogens).
Blueberries also contain small amount of Vitamin A & E that work as antioxidants to protect cells from free radical damage.
Blueberries contain polyphenols that help in regulation of inflammation. Some studies suggest blueberries increase natural killer (NK) cell activity, which helps fight infections and cancer cells.
Blueberries support gut microbiome. It contains soluble fiber and polyphenols that nourish beneficial gut bacteria.
How to consume Blueberries
Best option is to eat a handful fresh blueberries.
Blueberries can be add to smoothies, yogurt, or oatmeal.
Consume blueberry as tea. Add blueberries and green tea in hot water. It acts as an antioxidant.
Frozen blueberries also retain most nutrients, so can be used year-round.
Precautions
Very safe, but overconsumption may cause bloating in sensitive people due to fiber.
If person have diabetes eat small portions, though blueberries have a low glycemic index.
8. Pomegranate
The pomegranate (Punica granatum), is one of India’s most significant fruit crops in terms of commerce. It is indigenous to Iran.
How Pomegranate improve Immunity
Pomegranate also called a “superfruit” because it’s containing with potential secondary metabolites and nutrients that directly support immunity.
Peels, seeds and juices are all contain significant amount of secondary metabolite.
Pomegranate produces secondary metabolite such ellagitannins, anthocyanins, and flavonoids, that improve immune system, act as antimicrobial agents and reduce inflammation.
Pomegranate also act as a prebiotic, improve immunity by regulating the beneficial gut bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria.
Ellagitannins and Gallotannins are abundant in pomegranate and possess antimicrobial properties.
Anthocyanins, which give fruit color and and another metabolite catechins that have anti-inflammatory effects and act as antioxidant.
Ellagic acid and gallic acid act as strong antioxidants that control oxidative damage to cells.
Pomegranate contain Vitamin C that enhance the immunity and white blood cell production. It Improves skin texture and protect against infection by acting as mucous membrane barriers.
How to consume Pomegranate
Eat fresh seeds (arils) daily.
Drink fresh pomegranate juice and avoid packaged sugary ones.
Pomegranate can be added to salads, smoothies, or yogurt bowls.
Dried pomegranate seed powder (anardana) can be used as spice.
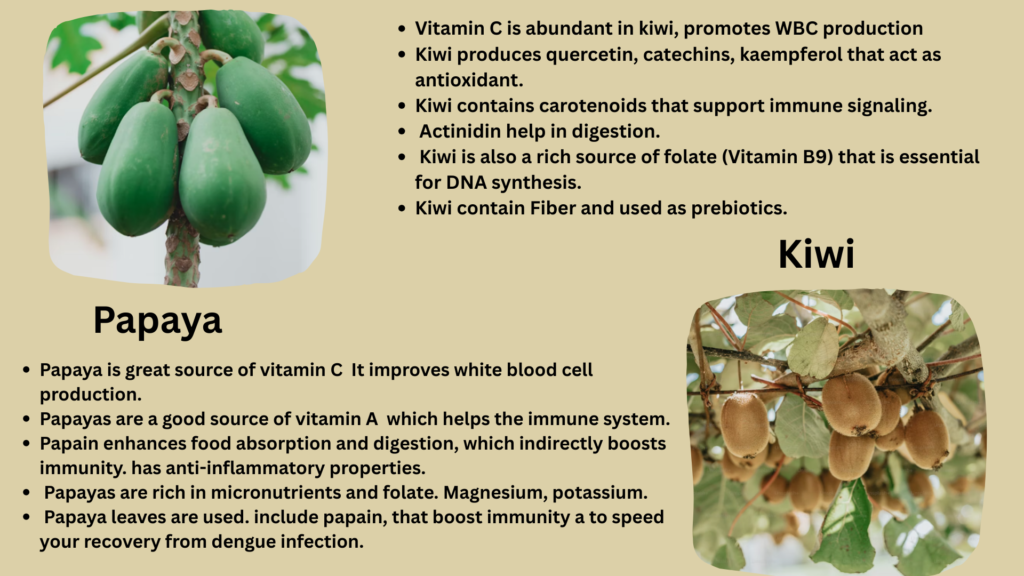
9. Papaya
Papaya scientific name is Carica papaya. It tastes sweet and has a soft texture that many find appealing.
Its silky texture and sweet taste appeal to a lot of people. Though more bitter than the fruit itself, the seeds can also be eaten.
How Papaya Boosts Immunity
Papaya is great source of vitamin C powerhouse. One medium size papaya gives more than 200 % of daily requirement.
It improves white blood cell (WBC) production, strengthens skin texture and mucosal barriers, the first-line defense.
Papayas are a good source of vitamin A (from β-carotene), which helps the immune system by maintaining healthy mucous membranes in the gut and respiratory systems.
Papain is a secondary metabolite and proteolytic enzyme that is present in papaya fruit and latex. enhances food absorption and digestion, which indirectly boosts immunity. has anti-inflammatory properties.
Papaya contain flavonoids and carotenoids function as antioxidants, shielding immune cells from harm caused by free radicals.
It promotes effective immunological signaling and lowers chronic inflammation.
Papayas are rich in micronutrients and folate. Magnesium, potassium, and folate all support a healthy immune system and metabolism. Folate helps in the production and repair of DNA in immune cells that divide quickly.
Traditionally, papaya leaves are used. include papain, phenolics, and alkaloids that boost immunity and platelet counts. used frequently to speed your recovery from dengue infection.
How to consume Papaya
Eat ripe papaya as breakfast fruit or mid-meal snack.
Papaya can be added to smoothies, fruit bowls, or salads.
Drink fresh papaya juice but if you are diabetic, avoid overripe papaya juice.
Papaya leaf extract is sometimes used in viral fevers to improve platelets.
10. kiwi
Kiwi (Actinidia deliciosa) is native to China. kiwi fruit is still found growing in the wild there.
How Kiwi Boost Immunity
Vitamin C is abundant in kiwis. More vitamin C (70–90 mg) than an orange can be found in one medium kiwi. promotes the development of white blood cells (WBCs). protects against infections by fortifying the mucosal and skin barriers.
Kiwi is high in vitamin E. protects immune cells from oxidative damage by acting as an antioxidant. increases the activity of T cells.
Kiwi produces flavonoids such as quercetin, catechins, kaempferol that act as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial.
Kiwi contains carotenoids such as lutein, β-carotene that support immune signaling and maintain mucosal health.
Actinidin is proteolytic enzyme produced in kiwi fruit that help in digestion, improves nutrient absorption and indirectly supports immunity.
Kiwi is also a rich source of folate (Vitamin B9) that is essential for DNA synthesis in rapidly dividing immune cells. Supports overall immune development and repair.
Kiwi contain Fiber and used as prebiotics. Kiwi contains soluble fiber and prebiotic oligosaccharides. Feed beneficial gut bacteria, this enhances immune balance.
Polyphenols found in kiwis reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines. maintains a balanced (not hyperactive) immunological response.
How to consume Kiwi
Eat raw kiwi slices and it is best in the morning or as a snack.
Add to smoothies, fruit salads, or yogurt bowls.
Blend with other citrus fruits for a Vitamin C immunity shot.
For kids or elderly, kiwi puree/juice is gentle and effective.