Lose weight the healthy way with science-based diet and fitness strategies.
What Does Healthy Weight Loss Really Mean?
Maintaining a healthy weight protect a person from many serious health conditions, including high blood pressure, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, gallstones, high cholesterol, fatty liver, joint pain, mental health issues, and certain types of cancer
People often confuse healthy weight loss with simple fat loss. Although they may look similar, they have different effects on the body in the long run.
Simple weight loss is usually fast, and through dieting, it is easy to lose more than 1 kg per week. However, such dieting often leads to muscle loss, rapid weight regain, and nutrient deficiencies.
Related article: Why Gut Health Matters: Secrets to a Happier, Healthier You
We will discuss the difference between healthy weight loss and simple weight loss.
Healthy weight loss
The main aim of healthy weight loss is to reduce stored fat (adipose tissue) while protecting and even building lean muscle mass.
Healthy weight loss leads to improved body composition, better metabolism, and protection against fat regain.
It is based on a low-calorie, nutrient-rich diet combined with regular strength training or exercise to build muscle.
It improves metabolism and reduces the risk of diabetes, heart disease, fatty liver, joint pain, and certain types of cancer.
It is not a fast method of losing weight, but rather a slow, healthy, and steady process of reducing 0.5 to 1 kg per week.
Simple weight loss
Simple weight loss often results in the loss of lean muscle, water, healthy fats, and other essential fluids because it is mainly based on dieting.
When you substantially reduce your calorie intake, your body prefers energy sources that are the simplest to break down—usually muscle and water over fat.
A person may lose weight more rapidly, but in the long term it affects both physical and mental health. Simple weight loss can cause nutritional deficiencies, weakness, and may lead to serious health conditions.
Weight loss from dieting is often not permanent, and there are high chances of regaining the lost weight in a short period of time.
Difference between Overweight and Obesity
Overweight refers to having excess bodily weight from muscle, bone, fat, and/or water. Obesity is defined as having a large quantity of excess body fat. Body mass index (BMI) is an effective indicator of overweight and obesity.
Why Quick-Fix Diets Don’t Work in the Long Run
It’s easy to try quick fix diets that promise quick results—such as low-carb fads, extreme calorie restriction, or juice cleanses. While these may cause rapid weight loss at first, the effects are rarely long-lasting.
Rapid weight loss is mainly caused by the loss of water and muscle tissue, rather than body fat. This makes it difficult to lose weight and decreases metabolism.
Quick fix diets frequently exclude key food groups, resulting in nutritional deficiencies in vitamins, minerals, and critical nutrients that your body needs to function.
Eating too few calories causes your body to preserve energy, making fat loss more difficult over time and resulting in weight gain once normal eating begins.
Strict rules can lead to cravings, binge eating, and guilt, making it challenging to have a good, balanced relationship with food.
Quick-fix diets focus rapid weight loss over general health and well-being, which can result in health issues like fatigue, muscle weakness, and poor digestion.
In contrast, healthy weight loss is achieved by balanced, adaptable eating habits that can be maintained over time. Instead of severe diets, focus on small, regular improvements that will lead to long-term results.
The Science Behind Calorie Balance and Metabolism
Weight loss is based on a basic principle: calories in, calories out. However, the way your body uses energy, known as metabolism, complicates the process beyond simply calculating calories.
If you eat more calories than you burn, your body stores the excess energy as fat (calorie surplus).
If you eat less calories than you burn, your body uses stored fat for energy (calorie deficit), resulting in weight reduction.
Walking, exercises, and strength training contribute to increased daily energy usage. Regular exercise not only burns calories but also protects muscle mass, which boosts metabolism.
Many people assume they have a slow metabolism is the reason of obesity however in most cases, weight gain is caused by calorie imbalance, inactivity, or bad eating choices, rather than a malfunctioning metabolism.
Note- Understanding calorie balance and metabolism allows you to make more informed dietary and activity decisions. Instead of extreme restrictions, aim to maintain a moderate calorie deficit, eat nutrient-dense foods, and keep active to support a healthy metabolism.
Top Nutrient-Dense Foods That Support Fat Loss
In Healthy weight loss, the objective is not to eliminate foods, but to prioritize nutrient-dense alternatives most of the time. Combining lean proteins, fiber-rich carbohydrates, and healthy fats results in meals that are both delicious and fat-loss friendly.
When it comes to weight loss, the quality of calories is as important as the quantity. Nutrient-dense foods contain vitamins, minerals, fiber, and protein without excess calories, making them perfect for fat loss and overall health.
Healthy fats such as almonds, sunflower seeds, green olives, chia seeds, flaxseeds, walnuts, avocados, butter, coconut oil, olive oil, nuts, and seeds are excellent alternatives for your diet.
Although some oils, such as olive oil, are regarded healthy, they also contain 9 calories per gram, as opposed to protein and carbohydrates, which have just 4 calories per gram.
Healthy fats such as almonds, sunflower seeds, green olives, chia seeds, flaxseeds, walnuts, avocados, butter, coconut oil, olive oil, nuts, and seeds are wonderful diet options.
Leafy greens and vegetables are low in calories but high in fiber, vitamins, water, and antioxidants. They add bulk to meals, allowing you to feel full without overeating, and they promote digestive health. Example: spinach, kale, lettuce, broccoli, cauliflower, peppers, and carrots.
Lean proteins and legumes Protein keeps you fuller for longer, helps maintain muscle mass, and has a high thermic impact, which means your body burns more calories while digesting it. Examples include chicken, turkey, fish, eggs, tofu, beans, chickpeas, and lentils.
Whole grains are high in fiber and give consistent energy while preventing blood sugar rises and reducing cravings. Examples include quinoa, brown rice, oats, and barley.
Fruits are naturally sweet and high in vitamins and fiber. Berries, are low in sugar yet abundant in antioxidants. Examples include berries, apples, and oranges.
How Protein, Fiber, and Healthy Fats Help You Stay Full
Protein, fiber, and healthy fats help you feel full by slowing digestion and influencing satiety hormones.
Protein is the most satisfying macronutrient, raising appetite-reducing hormones such as GLP-1 and keeping you feeling full for longer
Fiber adds bulk to the stomach, slows emptying, and activates satiety signals in the small intestine.
Healthy fats also affect hormone levels and lead to slowed digestion, which increases feelings of fullness.
Simple Portion Control Strategies That Actually Work
Smaller dishes, bowls, and glasses make standard-sized portions appear larger, allowing you to eat less while still feeling satisfied.
Instead of eating straight from a huge package, split your snacks into a dish or container to keep track of how much you’re eating.
Fill half your plate with veggies, one-quarter with lean protein, and one-quarter with whole grains or starches. Add a tiny amount of healthy fats, such as almonds or olive oil.
You can use your hand to approximate portion amounts.
Eat when you’re actually hungry, not merely bored, anxious, or out of habit. Stop when you are 80% full, but not stuffed.
Writing down what you eat will help you become more conscious of your behaviors and hold yourself accountable for your portion amounts.
Hydration and Its Role in Weight Management
Drinking plenty of water will help you lose weight by lowering your calorie intake, especially if you drink it before a meal.
Drinking plenty of water may also work by improving the burning of fat, which can help with long-term weight loss.
Drinking water has other weight loss benefits, such as keeping you hydrated when exercising and removing waste from your body.
Note- Choose black coffee, herbal tea, or water instead of artificial sugary drinks such as fruit juices and sodas because they contain a lot of empty calories. Instead,
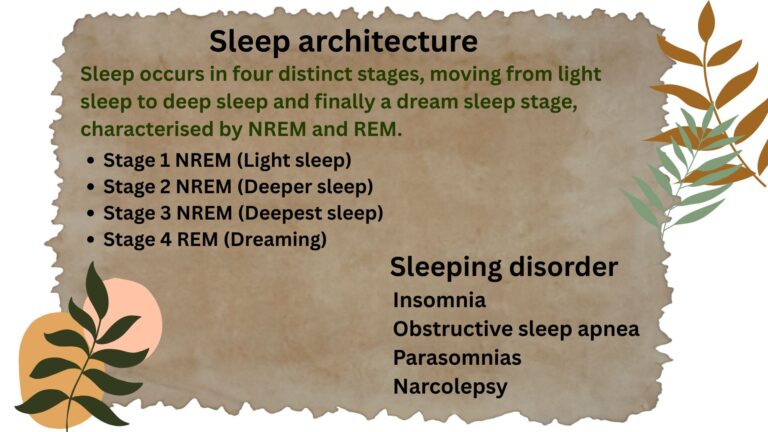
The Importance of Sleep and Stress Management in Weight Loss
Effect of insufficient sleep on weight loss
Insufficient sleep elevates ghrelin (the hunger hormone) and lowers leptin (the fullness hormone).
Imbalanced ghrelin and leptin levels cause increased appetite and cravings for high-calorie foods, poor metabolic efficiency, and less energy for exercise, making it difficult to lose weight and store less fat.
Lack of quality sleep can affect metabolic function and slow the rate of calorie burn, making losing fat more challenging.
Benefit of proper sleep
Adequate sleep and adequate stress management are essential for weight loss because they control hormones such as ghrelin and leptin.
Prioritizing 8 hours of excellent sleep can considerably help with weight loss by promoting metabolic balance and improving decision-making for healthier options.
Effect stress on Weight Loss
Chronic stress causes the release of cortisol, a hormone that promotes fat storage, particularly in the abdominal area.
Stress can lead to emotional eating, which is the utilization of food to cope with anxiety or stress, even when the person is not physically hungry.
High amounts of stress can affect the body’s metabolic activity and impede fat loss.
Benefit of no stress on weight loss
Invest in stress-reduction activities, such as mindfulness-based stress management programs, to learn healthier coping mechanisms and avoid emotional eating.
Common Weight Loss Myths You Should Stop Believing
Carbs are bad they make you fat
Carbohydrates are often labeled as ‘bad’ and blamed for weight gain, but not all carbs are unhealthy.
Refined carbs and added sugars can contribute to weight gain, whereas whole-grain carbs are nutritious and essential for your body’s energy and overall health.
Avoid fat
Healthy fats from sources like nuts, avocados, and olive oil help promote fullness and are an important part of a balanced diet.
Avoiding foods leads to weight loss
Skipping meals can slow down your metabolism and often leads to overeating later, making it harder to lose weight effectively.
Food with low fat is healthy
Low-fat or fat-free products may contain added sugars or unhealthy ingredients, while certain fats are actually beneficial for your health.
Tips to Stay Motivated Without Feeling Deprived
Make your objectives specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound in order to create clarity and a route to achievement.
Divide massive goals into smaller, achievable parts to make the entire process less intimidating and more approachable.
Create a daily plan or to-do list to help you stay focused and organized.
Daily exercise, even just taking a walk or stretching, can increase energy and attention.
Spend time doing exercises like meditation or deep breathing to cleanse your mind and lessen tension.
Give yourself little, delightful rewards when you finish a task or reach a milestone.
When to Seek Professional Help for Weight Management
Unexpected weight loss
Unexpected weight loss occurs when a person loses 5% of their body weight within 6 to 12 months. This is an alarming health condition that requires medical attention.
Overweight
Obesity or overweight is a major cause of many chronic diseases, including heart disease, low-density lipoprotein deposition, and diabetes. That requires medical attention.
Persistent health problems
If a person has a persistent health problem such as a heart disease, diabetes, or a fatty liver, he or she should seek medical attention while losing weight.
Eating disorder
If you have a history of eating disorders, you should get professional help for both your mental and physical health to ensure a safe and balanced approach to weight control.
Unsuccessful weight-loss attempts
If the person is unable to reduce significant weight, a healthcare expert can assist and support the weight loss journey.
How healthcare professional help
Personalized Health evaluation
A healthcare professional conducts a personalized evaluation, knows the patient’s health status, family history, and habits, and provides the best counsel for healthy weight loss.
A healthcare professional does a personalized evaluation of the patient’s health and advises on the best strategy to lose weight safely.
Monitoring and medical help
Person advised by a medical expert to seek correct therapy or undergo bariatric (weight loss) surgery. Professionals frequently monitor a person’s health and success in their weight loss journey.
Read article: